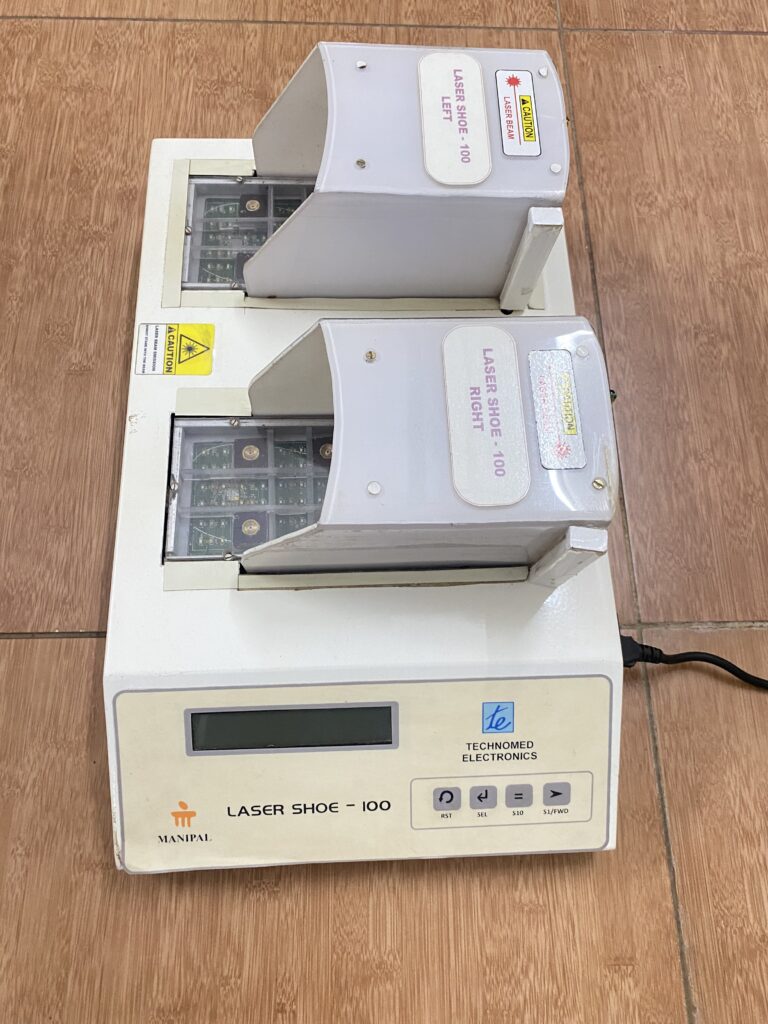
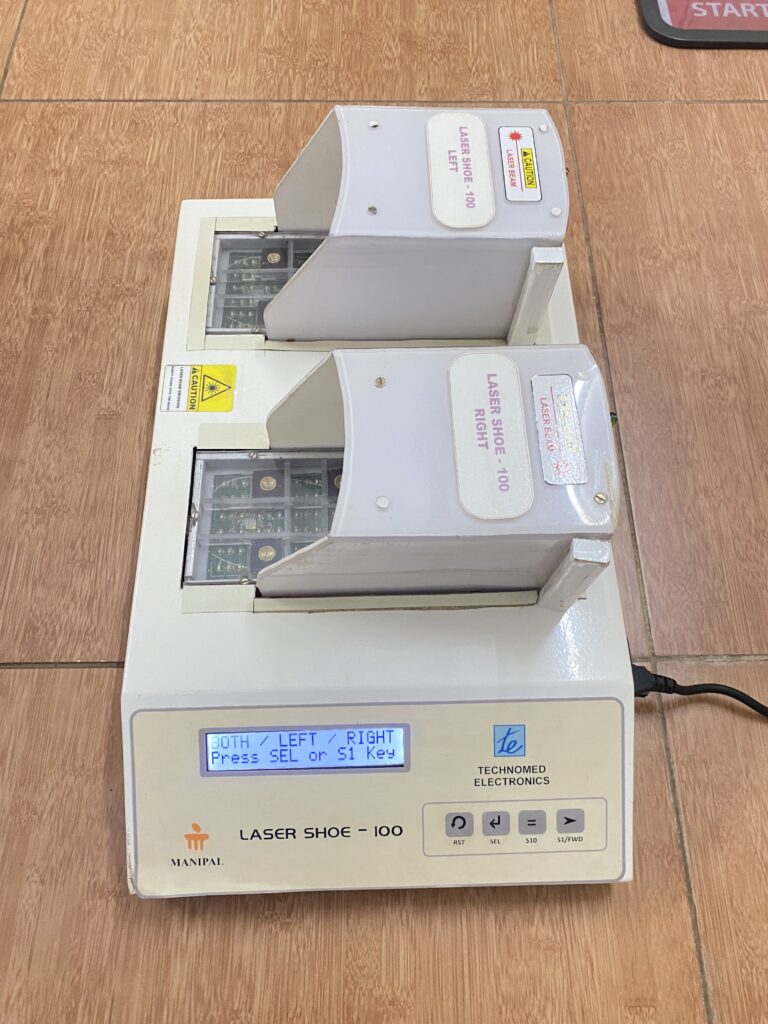
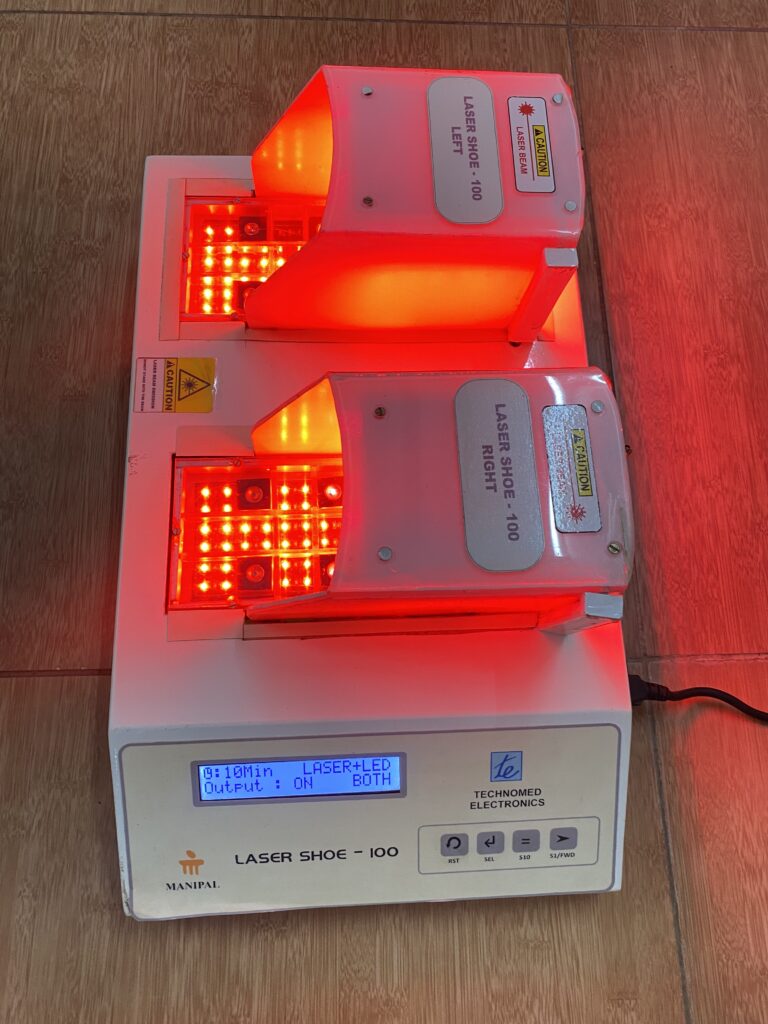
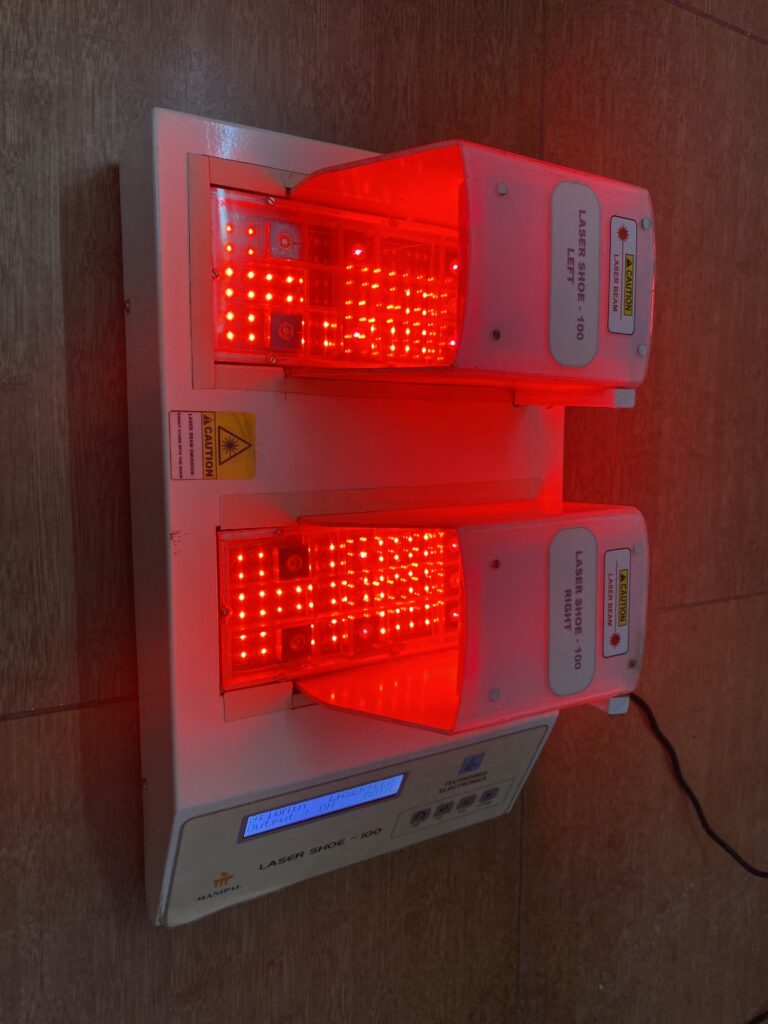
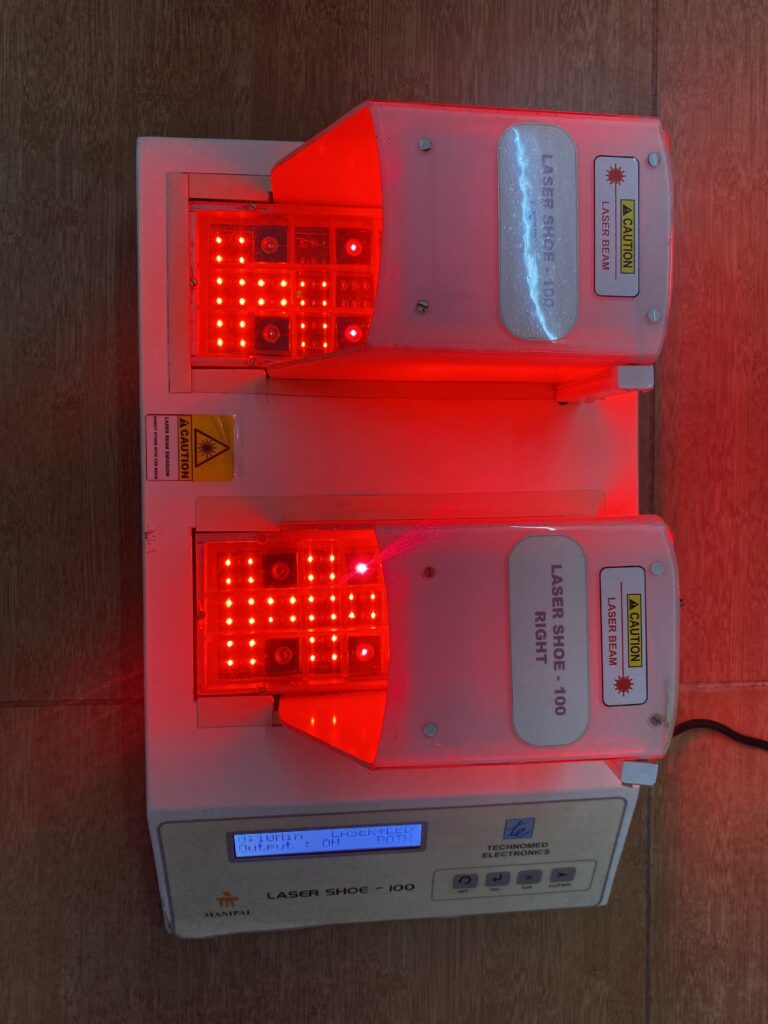
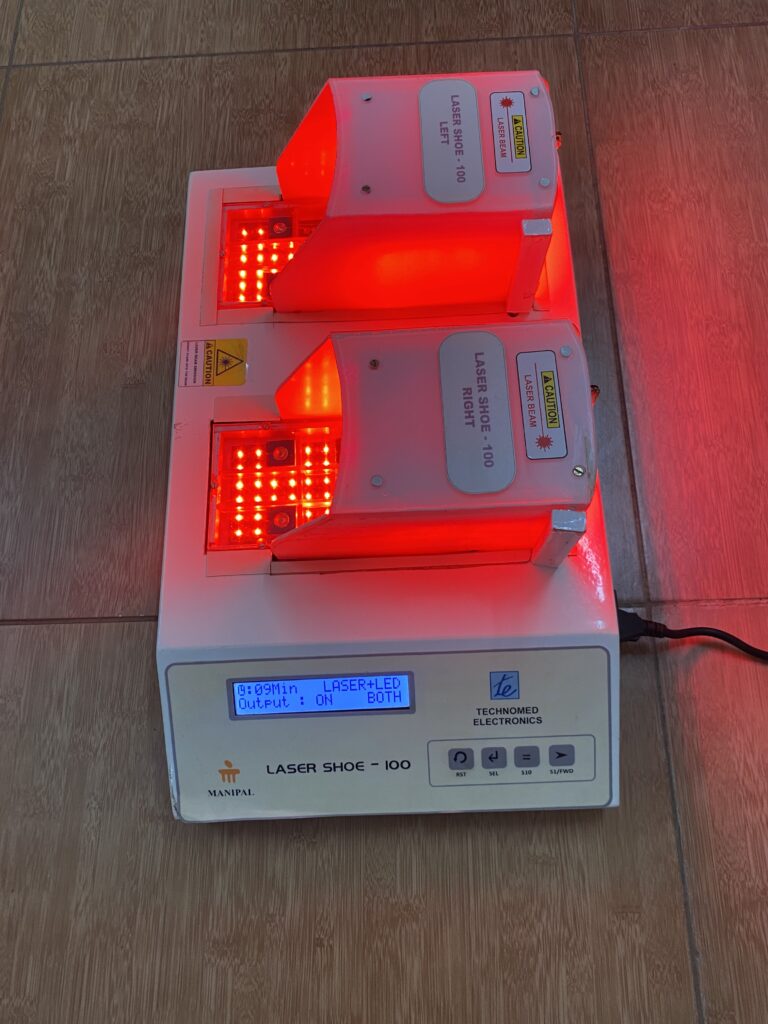
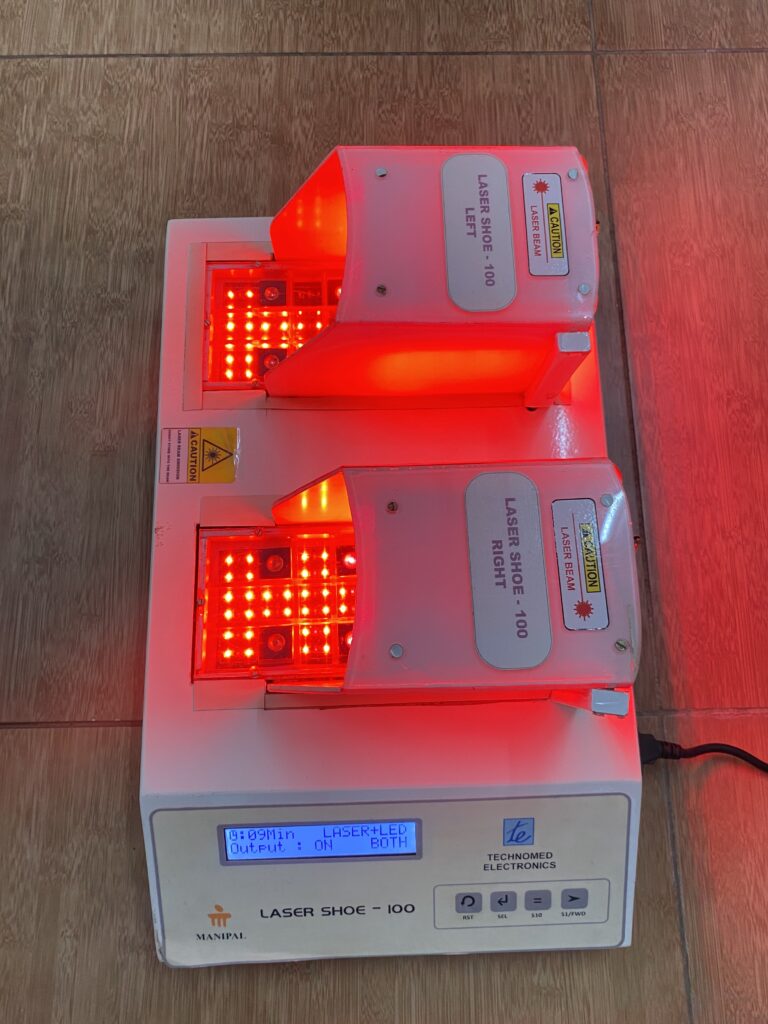
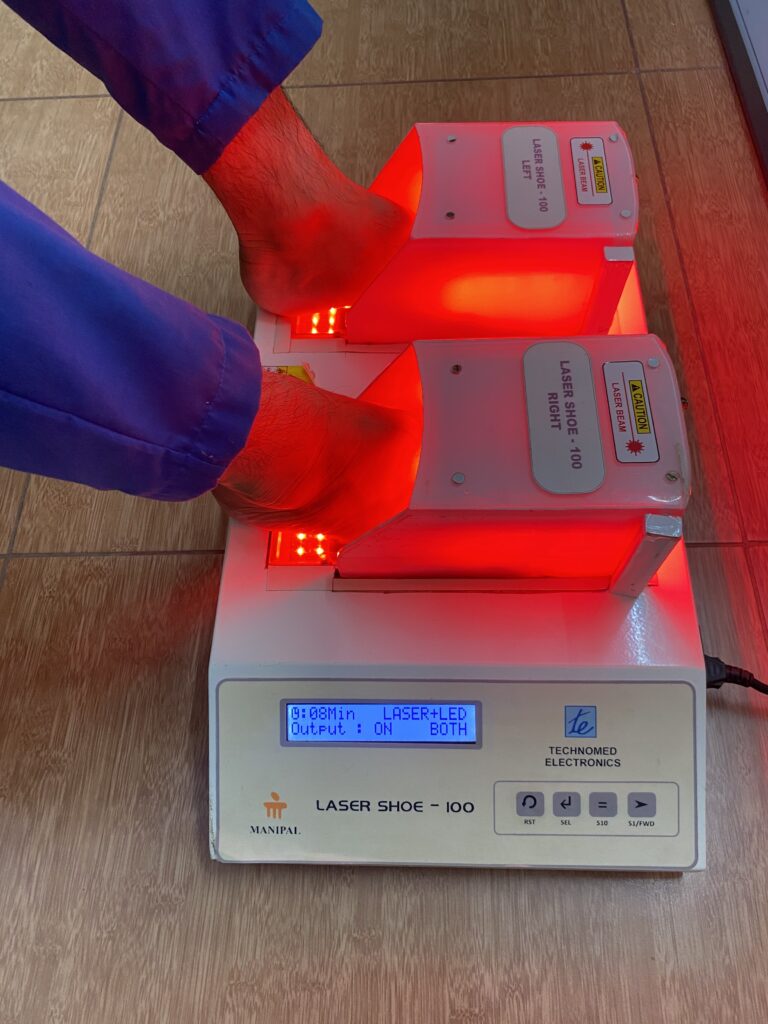
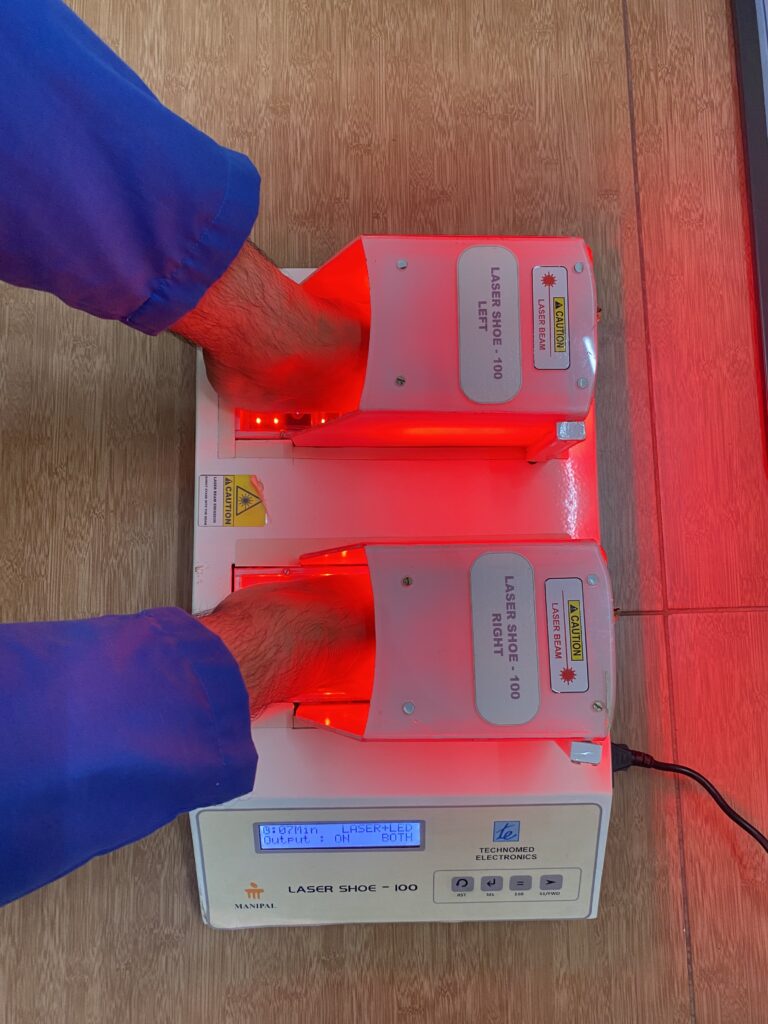
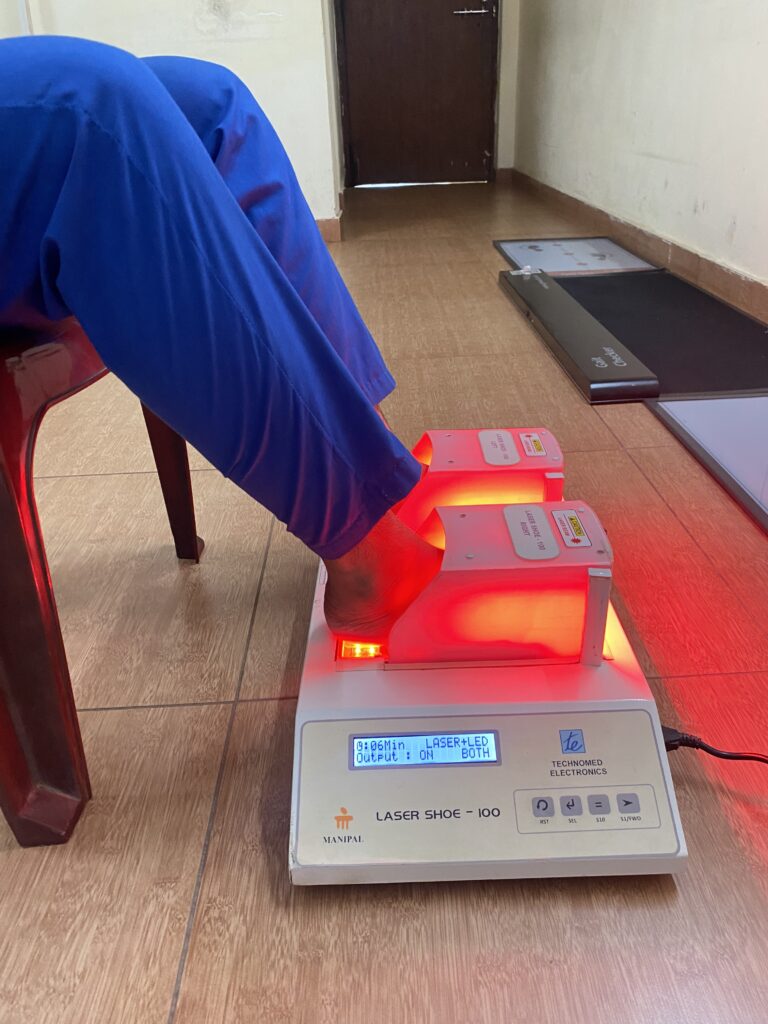
The innovation is non-pharmacological equipment for managing neuropathic pain. It is very cost-effective and easy to use both at the hospital and in community settings. The selection of LASER sensors in the dorsal and plantar aspect of the foot and the piezo-resistive force sensors are placed at predefined locations as shown in the figure in the preliminary data analysis section. These laser sensors are calibrated accordingly and placed on the sole for treating neuropathic pain.
Target users: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Pain
Application area: Unilateral/Bilateral feet (Plantar & Dorsal surface area)
The novelty of the device: The novelty of the system is to develop a cost-effective wearable LASER shoe, and the laser sensor is incorporated in the selected part of the foot region, which will be used to treat the neuropathic pain of a diabetic patient, thereby helping millions who suffer from this life-threatening disease at an affordable cost. In the proposed system, as the laser sensors are embedded into a shoe, this shoe can be put into the patients and used to treat a dorsal and plantar aspect of neuropathic pain. Apart from this, the problem of inconvenience and discomfort is caused to patients during the treatment in the supine and prone position in the existing method of scanning laser treatment for neuropathic pain.

Benefits/Impacts: The pharmacological approach for neuropathic pain management has its strengths and limitations. Neuropathic pain can alter the quality of life and the function of the individual. There is a need for a safe and novel approach to the management of diabetic neuropathic pain in diabetic individuals with a cost-effective approach at the community level.
About the background of the LASER SHOE Device:
Diabetes is a significant cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower limb amputation. One of the main complications of diabetes mellitus is diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The common symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy are burning, pin pricking, electric shocks, reduced sensations, etc., along with vascular and biomechanical changes.
Laser therapy plays a crucial role in the non-pharmacological management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. But most of the devices are imported and costly. Dr. G Arun Maiya, Chief Centre for Podiatry & Diabetic Foot Care and Research, MAHE, along with the Department of Science and technology-instrument Development program, the Govt of India, and the industry partner Technomed Chennai, developed a portable, affordable, and clinically validated LASER Shoe device for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This device was developed under the “Make in India” initiative by state-of-the-art technology, making laser technology more accessible and affordable to diabetic foot patients. This device was applied to patent rights. It brings down the treatment cost drastically up to less than 70%.
Application/ Procedure:
Before applying LASER Shoe, Detailed diabetic foot screening will be performed to evaluate the risk factors in the diabetic population. Neurological assessment includes a 10-gram monofilament, vibration perception threshold, vascular assessment like an ultrasound Doppler device, and biomechanical evaluations like manual muscle testing and plantar pressure measurement.
After a complete evaluation, the patient will be seated comfortably in a chair, and the laser shoe device will be placed under the patient’s feet. Appropriate parameters will be selected, and time will be selected as per the severity of the condition. Both sides of the feet will be irradiated with the laser beam. The laser shoe device emits a wavelength of 680nm with a total output of 5 to 20 Jules. This device works on the principle of photobiomodulation. It will increase peripheral vasodilation, increase axonal nerve recovery, and increase local metabolism by activating cytochrome biomarkers. We have found a significant improvement in neuropathic pain, local circulation at feet, reduction in plantar pressures, and improved quality of life.